DTIFIT
dtifit fits a diffusion tensor model at each voxel. You would typically run dtifit on data that has been pre-processed and eddy current corrected. Note that dtifit is not necessary in order to use the probabilistic tractography (which depends on the output of BedpostX, not dtifit).
Command-line interface
dtifit can be used from the command line (type dtifit and press Enter to get the usage).
dtifit --help
Compulsory arguments (You MUST set one or more of):
-k,--data dti data file
-o,--out Output basename
-m,--mask Bet binary mask file
-r,--bvecs b vectors file
-b,--bvals b values file
Optional arguments (You may optionally specify one or more of):
-V,--verbose switch on diagnostic messages
-h,--help display this message
--cni Input confound regressors
--sse Output sum of squared errors
-w,--wls Fit the tensor with weighted least squares
--kurt Output mean kurtosis map (for multi-shell data)
--kurtdir Output parallel/perpendicular kurtosis maps (for multi-shell data)
--littlebit Only process small area of brain
--save_tensor Save the elements of the tensor
-z,--zmin min z
-Z,--zmax max z
-y,--ymin min y
-Y,--ymax max y
-x,--xmin min x
-X,--xmax max x
--gradnonlin Gradient Nonlinearity Tensor file
Tip! The command line interface offers more options than the graphical interface
Graphical interface
Alternatively, in the FDT GUI, use the top left drop down menu to select "DTIFIT Reconstruct diffusion tensors".
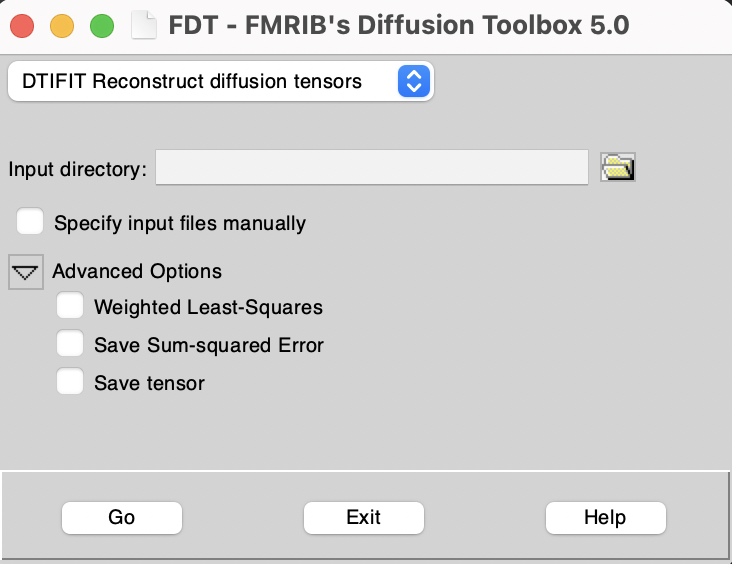
Inputs of dtifit
Required files are:
- Diffusion weighted data (
data.nii.gz): A 4D series of data volumes. This will include diffusion-weighted volumes and volume(s) with no diffusion weighting. - BET binary brain mask (
nodif_brain_mask.nii.gz): A single binarised volume in diffusion space containing ones inside the brain and zeroes outside the brain. - Output basename: User specifies a basename that will be used to name the outputs of dtifit. If the directory input option is used then the basename will be
dti. - Gradient directions (bvecs): An ASCII text file containing a list of gradient directions applied during diffusion weighted volumes.
- b values (bvals): An ASCII text file containing a list of b values applied during each volume acquisition.
Advanced options:
In addition to the required input above, the user can choose to apply a weighted least-squares regression instead of the default standard linear regression. The user can also choose to save the tensor elements and/or the sum of squared error. This last output can be useful for detecting artefacts.
Tip! On the FDT GUI, you can specify an input directory containing all the required files with standardized filenames, or alternatively you can specify input files manually by turning on the "Specify input files manually" switch. If an input directory is specified then all files must be named as shown in parentheses above. If input files are specified manually they can have any filename.
Outputs of dtifit
<basename>_V1- 1st eigenvector<basename>_V2- 2nd eigenvector<basename>_V3- 3rd eigenvector<basename>_L1- 1st eigenvalue<basename>_L2- 2nd eigenvalue<basename>_L3- 3rd eigenvalue<basename>_MD- mean diffusivity<basename>_FA- fractional anisotropy (isotropic ~ 0; stick-like ~1)<basename>_MO- mode of the anisotropy (oblate ~ -1; isotropic ~ 0; prolate ~ 1)<basename>_S0- raw T2 signal with no diffusion weighting
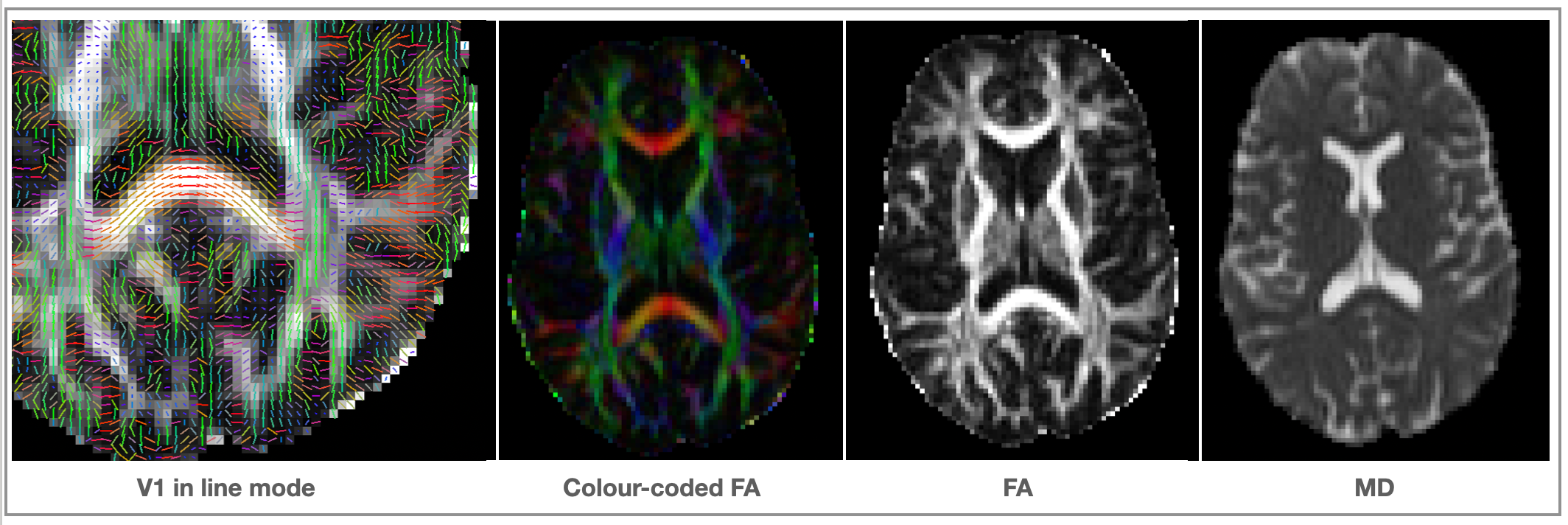
Optional output
<basename>_sse- Sum of squared error of diffusion tensor fit.<basename>_tensor- tensor as a 4D file in this order: Dxx, Dxy, Dxz, Dyy, Dyz, Dzz
Options only available from the command line:
-
--kurt: Adds a mean kurtosis to the fit (for multi-shell data), which is output in a<basename>_kurtfile. Note that fitting the mean kurtosis is different from the full kurtosis tensor model. -
--gradnonlin: If provided,dtifitwill consider the variability in the b-value and gradient orientation due to gradient non-linearities.