Handling and Inspecting Data from the Scanner
This mini practical covers Data Conversion to NifTI-MRS and how to quickly inspect your data. As with all these mini-practicals, instructions on how to run FSL commands can be found on the Getting Started page.
This example will help you understand how you can:
- Understand data that comes from the scanner
- Convert it to a useful and standardised format
- Inspect what the data shape, contents, and metadata are.
A particularly tricky part of MRS analysis is handling the disparate types
of data that come from different vendor's scanners, or even the many possible types
from the same scanner.
You can't just rely on file type to know what data is in a file.
This is why FSL-MRS uses the spec2nii tool to convert data to a standard format.
For this workshop we will hopefully be using data collected at the scanner on the first day, and the practical will guide you in using that data. However, in case that isn't an option, we have some pre-packaged Siemens data. If required, then click this button to go to the practical using the backup data.
Backup practical
If we are using data from the scanner then you can download it using the following button.
After downloading it unzip the contents into a directory called
marbel_data.
Data download
- Data Conversion to NIfTI-MRS
- Using the data collected in the workshop.
- Peek at your data
- Figuring our your data using the available tools.
- More on spec2nii
- A few extra details on spec2nii.
Data Conversion to NIfTI-MRS
What files should I use?
In this practical we will follow the conversion of two sets of data unedited PRESS and edited MEGA-PRESS. Data from a Philips scanner can come in many different formats: DICOM (classic and enhanced), SPAR/SDAT, data/list, and sin/lab/raw. The most frequently used in the research community is SPAR/SDAT, and we will use that. DICOM is also common, because it can be automatically archived to PACS. We will then follow the processing of this data through the following SVS processing stages.
Conversion using spec2nii
spec2nii is a command line too that comes with FSL for
converting SVS and reconstructed MRSI data to the standard NIfTI-MRS
format. Once in NIfTI-MRS we can process and visualise our data using
standard tools.
To get started cd into the appropriate data directory:
cd marbel_data/press_acc
Converting Philips .SPAR/.SDAT format
With spec2nii it is best to specify the type of file to the tool so as to expose all the options for that format. Run the following command to see the tool's interface
spec2nii philips --help
This shows us that there are a number of options, some which we will
use later for the MEGA-PRESS data. However, the basic interface is
spec2nii philips filename.SDAT filename.SPAR, with
-o and -f allowing you to specify the
output directory and output filenames.
Try this on the data in the folder. If you run ls,
you will see that there are two sets of data (four files, there
is an .SDAT and .SPAR for each set):
- ACC_PRESS_128_3_1_raw_act.{SPAR/SDAT} - The main acquisition
- ACC_PRESS_128_3_1_raw_ref.{SPAR/SDAT} - A water reference
spec2nii philips -o press_nifti -f metab_raw ACC_PRESS_128_3_1_raw_act.SDAT ACC_PRESS_128_3_1_raw_act.SPAR
Do the same with the dedicated water reference.
spec2nii philips -o press_nifti -f wref_raw ACC_PRESS_128_3_1_raw_ref.SDAT ACC_PRESS_128_3_1_raw_ref.SPAR
The data is now converted. We will look at what's in it after we've explored the spec2nii tools a little more.
Converting the MEGA-edited data
We will now convert the single-voxel MEGA-edited data we collected. It has the same format, and there are also four files (2 each for water reference and main acquisition) so we can use the same approach as above.
cd ../mega_acc
Now convert the data as before:
spec2nii philips -o nifti_edited -f metab_raw ACC_MEGA_320_4_1_raw_act.SDAT ACC_MEGA_320_4_1_raw_act.SPAR spec2nii philips -o nifti_edited -f wref_raw ACC_MEGA_320_4_1_raw_ref.SDAT ACC_MEGA_320_4_1_raw_ref.SPAR
Peek at the data
After converting the data, we can check its structure and any available metadata using the tools above. However, to validate that we have a) converted the right file, b) make decisions about the processing, or c) even find out what is in the file we might need to have a look at the spectroscopic data itself. There is a chance that even after conversion we might need to reorganise, split or combine bits of data before processing.
There is an MRS-specific command line tool for this
in FSL-MRS: mrs_tools. This commandline
tool can interrogate, visualise and manipulate NIfTI-MRS data.
Note: we will see more advanced visualisation tools in the next practical.
mrs_tools info
Let's use mrs_tools to look at the edited data we converted
from DICOM.
mrs_tools info nifti_edited/metab_raw.nii.gz
This produces a short summary of the data shape and some key, identifying meta-data
File metab_raw.nii.gz (.../nifti_edited) NIfTI-MRS version 0.9 Data shape (1, 1, 1, 1024, 320) Dimension tags: ['DIM_DYN', None, None] Spectrometer Frequency: 127.770744 MHz Dwelltime (Spectral bandwidth): 5.000E-04 s (2000 Hz) Nucleus: 1H Field Strength: 3.00 T
We see some expected values, 1H, 3,00 T, but we can also see that there is only a single dimension of data, 112 elements long, labelled as temporal averages (DIM_DYN). We know this is MEGA-edited data, so we expect a 2-element long DIM_EDIT dimension as well.
mrs_tools reshape
Let's use another of the mrs_tools commands to reshape this data
into one that has an editing dimension. mrs_tools reshape uses
Numpy-like reshaping to form new or remove unwanted dimensions.
mrs_tools reshape \
--file nifti_edited/metab_raw.nii.gz \
--shape -1 2 \
--d5 DIM_DYN \
--d6 DIM_EDIT \
--output nifti_edited \
--filename metab_reshaped
We can check that this has worked by using a visualisation command explained in the next practical.
mrs_tools vis nifti_edited/metab_reshaped.nii.gz --display_dim DIM_EDIT --no_mean
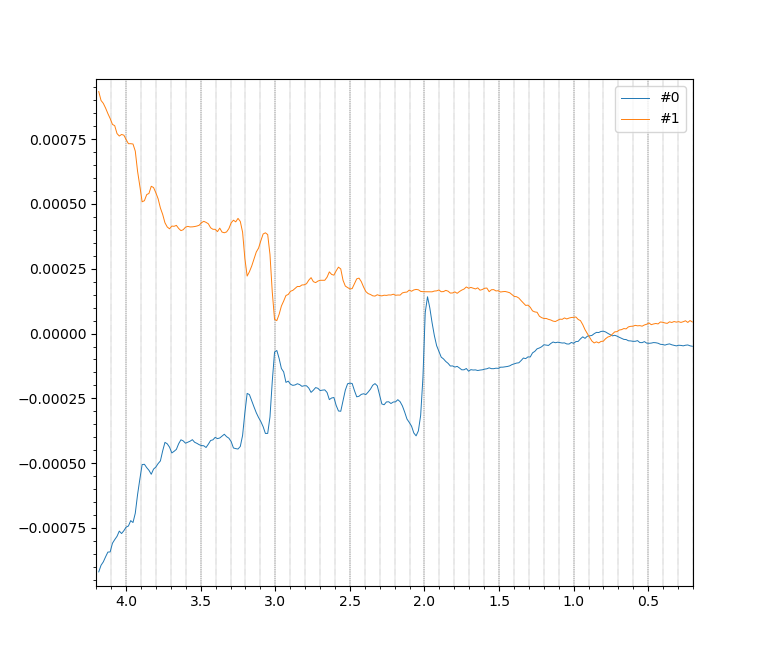
The output, showing two spectra, one with NAA (the peak at 2.0 ppm) suppressed,
indicates that we have successfully reshaped the data.
Note: The spectral baselines diverge strongly because of the
partially suppressed water interacting with deliberate phase cycling.
This is nothing to worry about.
We will see more of mrs_tools vis in later practicals
mrs_tools reorder
command to achieve this.
mrs_tools split and merge
Sometimes we collect data that we want to analyse together
in several separate acquisitions, perhaps so we can issue instructions
or check shim adjustments. In this case the tools mrs_tools split/merge
are useful.
Try splitting the data using mrs_tools split along the
temporal averages dimension DIM_DYN, before recombining it
using mrs_tools merge
mrs_tools split \ --file nifti_edited/metab_reshaped.nii.gz \ --dim DIM_DYN \ --index 79 \ --output nifti_edited \ --filename split
Check the file shapes using mrs_tools info
mrs_tools info nifti_edited/split_low.nii.gz mrs_tools info nifti_edited/split_high.nii.gz
Finally try recombining the files with an additional dimension.
This can be achieved by using the --newaxis flag
combined with the (generic) tag of the new dimension DIM_USER_0.
mrs_tools merge \ --files nifti_edited/split_high.nii.gz nifti_edited/split_low.nii.gz \ --dim DIM_USER_0 \ --newaxis \ --output nifti_edited \ --filename merged
Inspect the output
mrs_tools info nifti_edited/merged.nii.gz
to see a 28 (temporal averages) x 2 (edit) x 2 (new) piece of data ...
... Data shape (1, 1, 1, 1024, 80, 2, 2) Dimension tags: ['DIM_DYN', 'DIM_EDIT', 'DIM_USER_0'] ...
A short-cut
This reshaping (to a shape with N-dynamics x 2 edit condition) can be
achieved quickly using spec2nii. Try this now:
spec2nii philips \
-s 2 160 \
-t DIM_EDIT DIM_DYN \
-o nifti_edited -f reshaped_direct\
ACC_MEGA_320_4_1_raw_act.SDAT ACC_MEGA_320_4_1_raw_act.SPAR
We also don't need so many water reference dynamics, let's reduce this to one by running split.
mrs_tools split \ --file nifti_edited/wref_raw.nii.gz \ --dim DIM_DYN \ --index 0 \ --output nifti_edited \ --filename wref
More on Spec2nii
A few other formats
spec2nii handles a number of other formats. These include:
- Siemens DICOM
- Siemens .dat (TWIX)
- Siemens .rda
- United imaging DICOM
- Philips SPAR/SDAT
- Philips .data/.list
- Philips DICOM
- GE p-files
- jMRUI formats
- LCModel RAW format
- Bruker "fid" format
- Limited Varian support
The syntax for the most common of these are shown below as examples (no data provided).
Siemens DICOM
spec2nii dicom FILE_or_DIR
Siemens .data (TWIX)
spec2nii twix -e image .dat
Philips SPAR/SDAT
spec2nii philips .SDAT .SPAR
Philips DICOM
spec2nii philips_dcm .DCM
GE p-files / .7
spec2nii ge .7
Automatic conversion
spec2nii can attempt to automatically figure out the
correct conversion routine from the data using the auto
option. Note not all options and formats are exposed through this option.
spec2nii auto file.extension
Special conversion tools: spec2nii dump and anon
We can use spec2nii dump to inspect the detailed
meta-data contents of a converted NIfTI-MRS file. Do this now
for the unedited data we converted from twix format.
spec2nii dump nifti_edited/reshaped_direct.nii.gz
The first part of the output lists the NIfTI header, which contains
lots of infomration about the data size and the encoded orientation
(the latter is held in the various sform and
qform fields). The second part of the output contains
MRS-specific key:value pairs.
You might note that there are some (made up) patient identifying
fields in the second part (PatientDoB, PatientName, etc),
let's try removing these using spec2nii.
spec2nii anon nifti_edited/reshaped_direct.nii.gz -o nifti_edited -f anon spec2nii dump nifti_edited/anon.nii.gz
spec2nii has two sub-commands that allow you to
extract the header as an editable JSON file, before
insert(ing) the modified header bac into the file.
Now a preconfigured list of potentially sensitive fields have been removed.
More about spec2nii and NIfTI-MRS
spec2nii is developed by the authors of the FSL-MRS toolbox,
but it is also contributed to by the wider MRS development community.
If you find that your specific data format is not handled by the tool,
or it handles something incorrectly, then reach out to the developers on the
spec2nii development
page.
The NIfTI-MRS format was created by the
ISMRM
MRS study group, and the standard is both
published online
and has its own
documentation.
The NIfTI-MRS software tools (like mrs_tools) are published separately of FSL
and can be found in their own
Github repository.
A discussion of all the relevant tools and formats can be found in the paper NIfTI-MRS: A standard data format for magnetic resonance spectroscopy .